At SpeedX Marketing, we are a leading provider of innovative IT solutions tailored to meet your specific business needs. With years of expertise and a team of skilled professionals, we offer cutting-edge technology solutions that drive growth and efficiency.

Search has evolved dramatically over the past decade, driven by the rise of semantic web technology. Users now expect search engines to go beyond keyword recognition and understand natural language, along with the intent behind their queries. Google’s advancements in language processing have greatly enhanced its ability to deliver accurate results that match what users are genuinely looking for.
In the past, search engines were less sophisticated, and finding specific answers in a single click was uncommon. A query would often direct users to websites related to the keywords rather than providing a clear and relevant comparison or answer. Today, however, Google doesn’t just focus on matching keywords; it interprets the full meaning of a query to deliver the most relevant results. For example, instead of just returning links to websites, Google now often provides featured snippets that directly address the user’s question.
This shift marks the beginning of an era dominated by AI and semantic SEO. Unlike traditional SEO, which relied heavily on keyword stuffing, semantic SEO emphasizes understanding the context and meaning behind search terms. By focusing on user intent and the relationships between words, semantic SEO enables the creation of content that is both search engine-friendly and genuinely engaging for users.
Staying ahead in the ever-changing world of search engines means making your website friendly for semantic search. This guide will cover the fundamentals of semantic SEO and provide actionable advice to help enhance your website’s presence. Whether you’re running a small business, crafting blog content, or navigating online marketing, understanding semantic SEO is crucial for gaining an edge.
Semantic SEO is the process of optimizing your content by focusing on the broader topic rather than just a single keyword or phrase. It involves understanding user intent, improving user experience, and exploring the relationships between different concepts. This approach makes your content more relevant and useful to what people are actually searching for. Instead of only targeting specific keywords, Semantic SEO looks at the bigger picture of what users want to know and provides comprehensive, detailed information on that topic. This includes understanding user intent, creating content that answers questions fully, incorporating related topics, and using structured data to help search engines better interpret and deliver your content. Overall, Semantic SEO enhances the search experience by ensuring that content is aligned with users’ needs and delivers more accurate and meaningful search results.

For instance, if someone searches for “best hiking trails in Oregon,” semantic SEO would ensure that your content not only includes the keywords but also addresses related concepts, such as trail difficulty, scenic views, and seasonal recommendations. This helps search engines understand that your content is not just about hiking trails but is relevant to users looking for comprehensive trail information.
Semantic SEO is crucial for several reasons:
Incorporating Semantic SEO helps businesses not only meet the evolving expectations of search engines but also connect more effectively with their audience.
Semantic SEO evolved through key Google algorithm updates that refined how search engines understand and process search queries.
Over the years, Google has made significant strides in how it understands and responds to our search queries. One of the biggest advancements is the introduction of the Knowledge Panel. Initially, search engines focused on matching keywords, but now Google uses something called the Knowledge Graph to grasp the true meaning behind your searches.
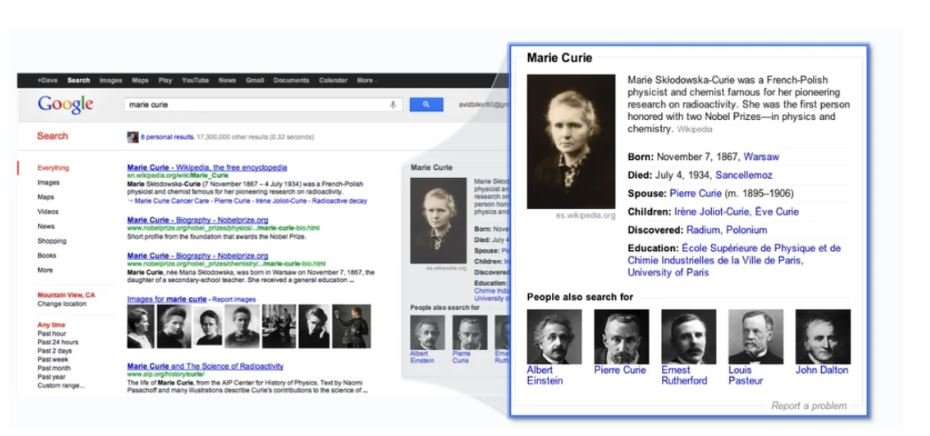
For example, if you search for “Star Wars,” Google doesn’t just look for those exact words. It recognizes that “Star Wars” could refer to the movies, the TV series, the characters, or even the franchise’s impact on pop culture. This intelligent approach allows Google to deliver more accurate and useful information.
The Knowledge Panel showcases this evolution by providing a snapshot of relevant details directly on the search results page. It pulls together information from various sources to give you a concise overview of what you’re looking for, whether it’s a person, place, or topic.
This shift from keyword-based search to understanding the context and relationships of information reflects how Google is making search more intuitive and relevant. It’s a key part of semantic SEO, which helps ensure that the content you see matches your real intent and enriches your search experience.
Google’s Hummingbird update, introduced in 2013, was a significant change to Google’s search algorithm. It focused on improving natural language search and made search results more precise and faster, especially for conversational or longer queries like those made on mobile devices.
The Hummingbird update, launched by Google in 2013, was a significant rewrite of its search algorithm. Its primary purpose was to enhance Google’s ability to interpret the meaning and context of search queries, rather than just focusing on individual keywords. By understanding the intent behind queries, Google could deliver more accurate and relevant results, especially for more complex, conversational queries where users ask questions in full sentences, as they would in everyday speech.
Key Features:
Hummingbird was a foundational update that improved Google’s ability to interpret and deliver more accurate search results based on the meaning behind queries. It paved the way for later advancements, such as the BERT and RankBrain updates, which continue to refine Google’s ability to understand and respond to the intent behind searches, making the search experience more user-friendly and relevant.
RankBrain, introduced by Google in October 2015, is an advanced component of the search algorithm that leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve search result relevance. Its main role is to handle novel or ambiguous queries by relating them to known data and patterns, thereby enhancing the quality of search results.
The algorithm functions by converting search queries into mathematical representations called “vectors” using machine learning. This process helps RankBrain interpret the context and intent behind searches, even those that are new or unclear. It compares these queries to similar ones from its database to predict and deliver the most relevant results. RankBrain continuously learns from user interactions, refining its understanding and improving accuracy over time. It excels in managing ambiguous queries by matching them with previously processed ones to provide appropriate search results.
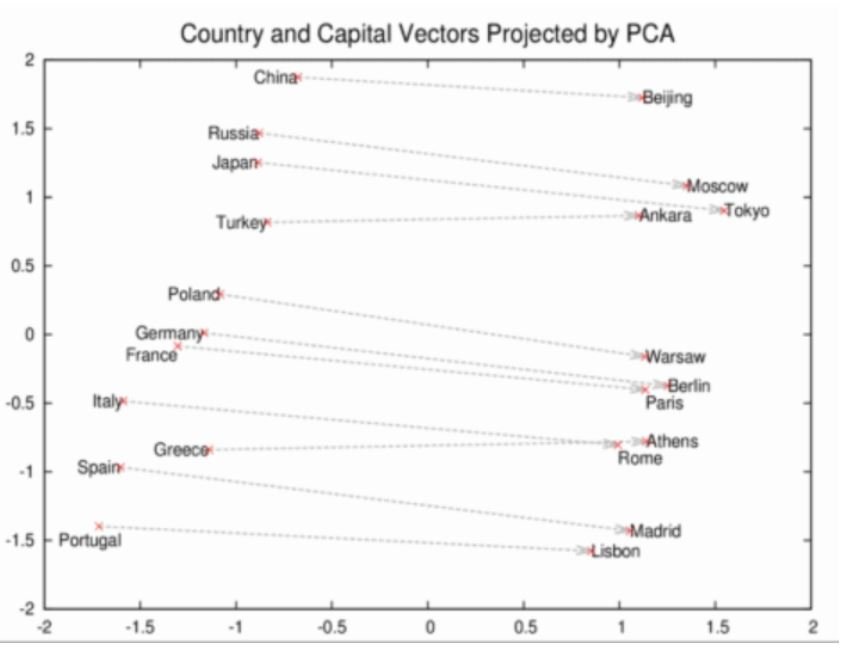
RankBrain uses technology like ‘Word2vec’ to transform keywords into concepts. For instance, it recognizes that ‘Paris’ and ‘France’ relate as ‘capital and country,’ similar to ‘Berlin’ and ‘Germany,’ but not like ‘Madrid’ and ‘Italy.
Key features of RankBrain include its reliance on machine learning for interpreting queries, its ability to understand the semantics behind search terms, and its indirect contribution to personalized search results. Unlike traditional algorithms with fixed rules, RankBrain adapts and evolves based on new data and interactions.
RankBrain significantly impacts search results by enhancing their relevance and effectively handling new queries, which constitute about 15% of daily searches. This shift has led to a change in SEO strategies, moving from keyword-focused approaches to optimizing for user intent and broader topics. Overall, RankBrain represents a major advancement in search technology, improving accuracy and user experience through its sophisticated handling of complex queries.

BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) is a machine learning model developed by Google that helps search engines understand the context of words in a sentence by analyzing them in both directions (from left to right and right to left), unlike traditional models that process words in a fixed sequence. This allows BERT to grasp the full meaning of queries, especially when dealing with complex or ambiguous language. For example, if someone searches “best way to care for leather shoes in rainy season,” BERT can recognize that “care for” is connected to “leather shoes” and “rainy season” influences the type of care needed. BERT’s understanding of language is deeply tied to NLP (Natural Language Processing), which enables machines to process human language in a way that mimics human understanding. RankBrain, an earlier algorithm, helped Google understand user intent by analyzing patterns, but BERT goes a step further by improving the semantic understanding of individual queries, making it more effective for semantic SEO. This connection allows search engines to match web content more accurately to the searcher’s intent, improving search results. By analyzing sentences holistically, BERT ensures more relevant and contextually correct answers are served up in searches. For instance, if a user types “who’s on the $100 bill,” BERT helps the engine understand the user is looking for the person on the bill, delivering the right answer (Benjamin Franklin) instead of irrelevant information about the $100 bill itself.
Traditional SEO primarily revolves around optimizing content for specific keywords and phrases, often focusing on keyword density and meta tags. However, Semantic SEO goes beyond this by emphasizing the meaning and context behind the words used in content.
Here are the major differences:
In essence, Semantic SEO represents a more sophisticated approach to optimizing content, focusing on delivering valuable and contextually relevant information to users, while Traditional SEO remains rooted in keyword optimization and technical aspects.
By focusing on the meaning behind the keywords and creating content that meets users’ needs more holistically, you can significantly enhance your website’s visibility and rankings. Ready to take your SEO strategy to the next level? Let’s dive into the seven best practices for Semantic SEO that will help you achieve better rankings.

To optimize for semantic SEO, it’s essential to focus on creating content that directly addresses the needs, questions, and intent of your audience. Rather than stuffing keywords into content, the key is to answer the searcher’s query comprehensively and naturally. For example, Backlinko conducted a case study where they improved organic traffic by 49% by focusing on “topic clusters” instead of individual keywords. They reorganized their blog posts into interconnected topics, ensuring each piece of content provided in-depth answers to user queries. This approach is effective because semantic SEO prioritizes content that answers specific questions within a broader context, meaning search engines are looking for depth and relevance rather than keyword frequency.
For instance, if your website is about “vegan diets,” instead of writing multiple short posts targeting specific keywords like “vegan breakfast” or “vegan lunch ideas,” create comprehensive guides that cover these topics in depth, linking between related sections. A successful case is HubSpot, which saw a boost in search rankings by using pillar pages—long, detailed articles that serve as the central hub of a topic, with smaller, related articles linked to them. This strategy aligns with semantic SEO because it reflects how search engines like Google now understand not just isolated keywords but the overall topic relevance, intent, and structure of the content.

To effectively optimize for semantic SEO, focusing on medium-tail keywords is crucial, as these phrases strike a balance between specificity and search volume, allowing for broader audience engagement. Unlike short-tail keywords that may be too general or competitive, medium-tail keywords provide the opportunity to create content that is topically relevant and rich in context. For example, instead of targeting a broad term like “travel,” one might focus on “best eco-friendly travel destinations,” which not only narrows the audience but also invites a deeper exploration of the topic. By crafting content that answers specific questions related to these medium-tail keywords—such as discussing sustainable practices in travel, local cultures, and unique experiences—websites can improve their chances of ranking higher in search results. This approach not only enhances visibility but also establishes authority within the niche, as the content resonates with users’ intent and provides valuable insights that cater to their needs. Engaging users with in-depth articles, guides, or case studies around these targeted keywords fosters a more meaningful connection, ultimately driving organic traffic and improving overall SEO performance.
Understanding user intent is the cornerstone of Semantic SEO. This involves identifying whether the user’s query is informational (seeking knowledge), navigational (looking for a specific site), or transactional (intending to purchase). By tailoring your content to match the specific intent, you can enhance user satisfaction and improve your rankings. To excel in Semantic SEO, it’s essential to grasp the intent behind user queries.

Here’s how to do it:
Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to identify the keywords your target audience is using.
Use tools like Google Search Console and keyword research tools to understand the types of queries users are making. Look for patterns in the questions they ask and the language they use.
Develop detailed profiles of your target audience. Understand their needs, preferences, and pain points to tailor your content accordingly.
Track how users interact with your content. Pay attention to metrics like bounce rate, time on page, and conversion rates to gauge how well your content meets user intent.
Use social media, forums, and comments sections to engage with your audience. Listen to their feedback and questions to refine your content strategy.
Suppose, If your target keyword is “buy running shoes,” the intent is clearly transactional. Your content should focus on showcasing different running shoe options, providing purchasing links, and highlighting the benefits of each product. On the other hand, if the keyword is “best running shoes for beginners,” the intent is informational, and your content should offer a comprehensive guide to choosing the best shoes for new runners.
By focusing on what users really want, you can create more relevant and valuable content that resonates with your audience and ranks higher in search results.
Creating a detailed content outline is crucial for effective Semantic SEO. A well-structured outline helps ensure your content is comprehensive, logically organized, and easy to read.

Here’s how to make it work:
Start by identifying the main topics related to your industry or niche. Use tools like Google Trends, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to find popular subjects and related queries.
Break down core topics into subtopics that cover various aspects of the main theme. This helps in addressing different facets of the subject, improving your content’s relevance and comprehensiveness.
Instead of targeting individual keywords, create clusters of related terms. For example, if your core topic is “digital marketing,” related clusters might include “SEO strategies,” “content marketing,” and “PPC advertising.”
Organize your content into a clear hierarchy with headings, subheadings, and bullet points. This helps both users and search engines navigate your content more effectively.
Enhance your content with images, videos, infographics, and other media that add value and context. This makes your content more engaging and informative.
Use structured data to provide additional context to search engines. Mark up elements like FAQs, product reviews, or event details to improve visibility in search results.
Suppose, you’re writing about “benefits of meditation,” your outline might include sections on “physical benefits,” “mental health benefits,” “different types of meditation,” and “how to start meditating.”
By focusing on creating detailed content outlines, you can significantly improve your site’s search engine rankings and deliver more valuable content to your audience.
Creating detailed content is crucial for Semantic SEO. This means going beyond superficial coverage of a topic and providing in-depth, comprehensive information.

Here’s why and how you should approach this:
Write in a natural, conversational tone. Search engines are increasingly adept at understanding and processing natural language, so content that mimics human conversation is more likely to perform well. Use synonyms, variations, and contextually relevant phrases throughout your content.
Ensure your content thoroughly covers the topic. Address various aspects, answer potential questions, and provide valuable insights. For instance, a blog post about “healthy eating” should cover nutrition facts, meal planning, benefits, and common misconceptions.
Incorporate Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords—terms related to your main keywords that help Google understand the content’s context. For example, for a page about “home workouts,” LSI keywords might include “exercise routines,” “fitness at home,” and “bodyweight exercises.”
Organize your content with clear headings, subheadings, and bullet points. This not only improves readability but also helps search engines grasp the structure and key points of your content.
Incorporate multimedia elements like images, videos, and infographics to make your content more engaging and informative. Ensure these elements are optimized with relevant alt text.
Regularly update your content to reflect new information and trends. Expanding existing articles with new insights or recent developments can help maintain their relevance and authority over time.
Aim to create content that answers common questions in a format that can be easily picked up for featured snippets. This might include using bullet points, numbered lists, or concise definitions.
By providing detailed content, you can create more relevant and engaging material that resonates with both users and search engines.
Optimizing for multiple keywords, also known as semantic keywords, involves targeting related terms and variations that support the main topic. Rather than focusing solely on a single keyword, consider a range of related terms and phrases that users might search for. This approach aligns with the principles of semantic search, which seeks to understand the broader context of user queries.

Suppose
Here’s how to Optimize for Semantic Keywords:
Use tools like Google Trends, keyword research tools, and competitor analysis to identify terms related to your main keyword.
Include semantic keywords in a way that flows naturally within your content. Avoid keyword stuffing by focusing on relevance and readability.
Develop content around themes rather than just keywords. For instance, if your main keyword is “organic skincare,” you might create sections on different types of products, benefits, and user testimonials.
Incorporate semantic keywords into meta titles, descriptions, and headers to reinforce the context of your content.
By embracing Semantic SEO and optimizing for multiple keywords, you not only enhance the relevance of your content but also align with the advanced capabilities of modern search engines, leading to better rankings and increased visibility.
The “People Also Ask” (PAA) feature in Google search results presents a valuable opportunity to target additional queries related to your main topic.
Here’s how to effectively incorporate PAA into your Semantic SEO strategy:
Use tools like AnswerThePublic, SEMrush, or directly search on Google to find common PAA questions related to your topic.
Seamlessly weave answers to these questions within your content. This can be in the form of FAQ sections, headings, or within the main body of your article.
Google often features snippets that provide clear and concise answers. Aim to answer the question directly within the first few sentences of the relevant section, followed by more detailed information.
Implement FAQ schema to help Google understand the Q&A format of your content, increasing the chances of appearing in rich snippets.
Don’t just stop at answering the question. Provide additional insights and related information that adds value and encourages further reading.
By following these Semantic SEO best practices and effectively answering “People Also Ask” questions, you can significantly enhance your website’s visibility and ranking potential. Embrace the future of SEO and watch your digital presence grow!
To harness the power of semantic SEO and improve your search rankings, it’s essential to adopt specific best practices. One of the most effective strategies is topic clustering, a method that organizes your content into related groups to signal to search engines that your site comprehensively covers particular subjects.
Topic clustering involves creating a central “pillar” page that provides a broad overview of a topic and then linking it to more detailed “cluster” content pieces that delve deeper into subtopics. This structure not only enhances the user experience but also signals to search engines that your content is authoritative and relevant.
Here’s how to implement it effectively:
Determine the primary topics that are most relevant to your audience and industry. For example, if you run a fitness blog, core topics might include “strength training,” “cardio workouts,” and “nutritional advice.”
Develop comprehensive, high-quality content that serves as the cornerstone for each core topic. Pillar content should be detailed and provide a broad overview of the topic.
Create supporting articles that delve into subtopics related to the pillar content. These cluster pieces should link back to the pillar content and to each other, creating a network of interconnected pages.
Use strategic internal linking to connect pillar content with cluster articles. This helps search engines understand the relationship between topics and improves navigation for users.
Regularly analyze your content performance and adjust your topic clusters based on user engagement and SEO metrics. This ensures your content remains relevant and effective.
This holistic approach ensures that your SEO efforts are aligned with the evolving needs and expectations of both users and search engines.
Structured data is a standardized format for providing information about a page and classifying the page content. It helps search engines understand the context and content of your pages better.

Here’s how to leverage structured data effectively:
Implement schema markup to provide detailed information about your content. This can include information about products, reviews, events, and more. Schema.org is the most commonly used vocabulary for this purpose. By using schema markup, you help search engines display rich snippets in search results, which can improve visibility and click-through rates.
Structured data helps generate rich snippets—enhanced search results that include additional information like star ratings, product prices, and review counts. These snippets attract more attention and can lead to higher click-through rates.
By providing structured data, you make it easier for search engines to understand and index your content. This can lead to better rankings, as search engines can more accurately match your content with user queries.
Search engines regularly update their guidelines and best practices for structured data. Stay informed about the latest changes and ensure your structured data is always up-to-date to maintain optimal performance.
By integrating Semantic SEO strategies and structured data into your content approach, you’ll not only improve search engine rankings but also deliver a more meaningful experience to your audience. This comprehensive approach helps ensure that your content is both relevant and easily understood by both users and search engines.
Harnessing the power of Semantic SEO can be made easier with these popular and free tools. To effectively implement Semantic SEO, leveraging the right tools can make a significant difference. Here are some popular and free tools that can help:
Google Autocomplete is a feature that suggests search queries as you type in the Google search bar. This tool provides insights into popular search terms and queries related to your topic. By analyzing these suggestions, you can identify relevant keywords, variations, and questions that users frequently search for. This helps you tailor your content to address these queries and improve its relevance. Here’s how to use It:
How It Helps:
Google Related Searches appear at the bottom of the search results page and provide additional search terms related to your query. This tool helps you understand what other topics or questions users are interested in. Incorporating these related terms into your content can enhance its relevance and cover a broader range of user queries. Here’s how to use It:
How It Helps:
Answer The Public is a tool that generates a visual representation of questions and phrases related to your keyword. It helps you understand the types of questions people are asking about a topic and provides valuable insights into user intent. By addressing these questions in your content, you can better meet user needs and improve your semantic relevance. Here’s how to use It:
How It Helps:
By harnessing these tools and focusing on the intent behind search queries, you can craft content that resonates with users and aligns with the principles of Semantic SEO. Embrace this approach to enhance your search visibility and deliver valuable, context-rich content.
Embracing Semantic SEO can transform your approach to content creation and optimization. By focusing on the intent behind searches and using the right tools, you can craft more engaging and relevant content that resonates with both users and search engines.
Semantic SEO is a strategic approach that focuses on enhancing the meaning and context of content to align more closely with user intent and search engine understanding. Unlike traditional SEO, which often prioritizes keyword frequency, semantic SEO emphasizes the importance of creating comprehensive, topic-rich content that addresses the nuances of user queries. By leveraging structured data, synonyms, and related concepts, semantic SEO helps search engines better interpret the relevance of web pages in relation to a user’s search, ultimately leading to more accurate results. This approach not only improves visibility in search engine results but also enhances the user experience by providing meaningful, valuable information. As search engines evolve to become more adept at understanding natural language and context—thanks in part to advancements like BERT—embracing semantic SEO becomes increasingly essential for businesses looking to establish authority, drive organic traffic, and foster lasting connections with their audience. Through this method, websites can effectively answer complex queries and satisfy user needs, ensuring they remain competitive in the ever-evolving digital landscape.